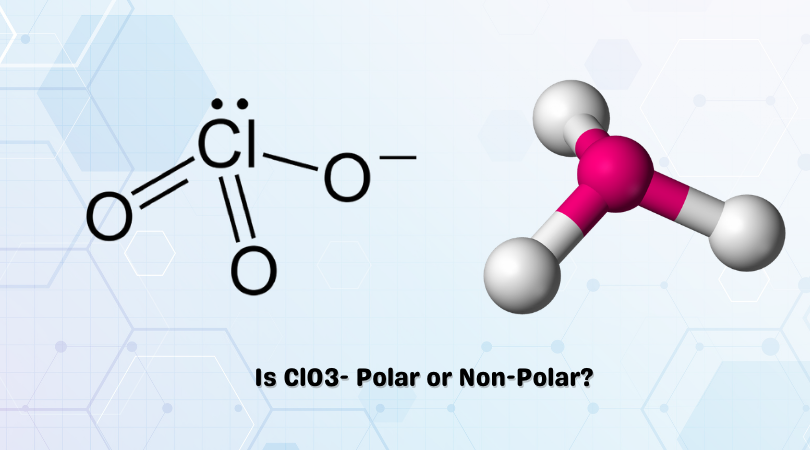
The chemical formula ClO3– represents Chlorate ion. Chlorine can reach oxidation states of +1, +3, +5 and +7. In this case, as seen in the figure, Chlorates exist in a +5 oxidation state. With an abundance of oxidizing elements, the Chlorate ion and its salts make for powerful oxidizing compounds.
The structural properties of ClO3- will help us understand its polarity better.
Polarity: What is it?
Due to electronegativity and individual charges, atoms share their electrons in an unequal manner. This leads to a separation of charges and the formation of an electric dipole. Polarity is the phenomenon where charges are separated to form an electric dipole moment.
Polar and Non-polar bonds are determined on the basis of the electronegativity of individual atoms.
A polar molecule will have a net dipole moment due to the presence of induced charges caused by electronegativity of atoms. A non-polar molecule has a zero net-dipole moment.
The polarity of a molecule depends on its shape, its electronegativity and its net dipole moment.
ClO3- Polar or Non-Polar?
ClO3– has a trigonal pyramidal shape with a lone pair of electrons over the Chlorine atom. It has bond angles of 109.5°, formed due to the repulsion explained by VSEPR theory. A lack of symmetry due to its geometry results in the induced charges not being cancelled out.
This points to a polar nature.
Electronegativity and Net Dipole Moment
In terms of electronegativity, the Chlorate ion possesses a negative ionic charge of -1. The difference in charge between Chlorine and Oxygen is 0.38. This suggests that the bonds between the atoms are non-polar in nature. However, the presence of a negative ionic charge over the atoms, makes the Cl-O bonds polar in nature.
The net dipole moment is given by:
Cl charge= 0.510
O charge=-0.503
O charge=-0.503
O charge=-0.504
with a dipole moment of 2.18 Debye
With a non-zero dipole moment, the ClO3– ion is a polar molecule.
CONCLUSION
Due to its asymmetrical shape and the presence of a net dipole moment, the ClO3– ion is polar in nature. This affects its solubility and other properties.