Tungsten is an extremely hard metal used in machinery, rockets, and abrasives. The name ‘Tungsten’ comes from a Swedish namesake meaning—heavy stone. In contrast, Tungsten is symbolized by the letter ‘W’ due in part to its discovery in the mineral Wolframite. The element is almost exclusively found in ores/minerals.
Tungsten possesses a number of remarkable physical properties. The element’s melting point of 3410°C is the highest among all known elements barring Carbon. Tungsten also has the highest boiling point at 5930°C and a density comparable to that of Gold and Uranium.
With that out of the way, let’s look into a lesser-known property of Tungsten- its magnetism.
Contents
Magnetism Explained

The magnetic properties of elements in the periodic table is well documented. We have been familiarized with magnetism through middle school experiments with bar magnets and iron filaments.
The origin of this magnetic behavior lies in the electrons inside of the atom. The electrons in the atom possess a magnetic moment by virtue of their movement about an axis and around the nucleus. This results in a magnetic dipole that is the source of magnetism.
A moving charge, say an electron, is capable of generating a magnetic field leading us to believe that electrons are tiny magnets. However, the orientation of electrons in most materials is random, resulting in zero net magnetic fields. Elements are classified as paramagnetic or diamagnetic based on their magnetic properties.
The magnetic permeability (Km) of an element is a quantity that essentially measures the response of materials to an applied magnetic field. Km =1 if the material does not respond to the magnetic field. Electrons or ions do not get oriented as they do in a magnet and therefore do not respond to the applied field. A positive relative permeability more significant than 1 implies that the material magnetizes in response to the applied magnetic field. The table[1] lays out the magnetic permeability of paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials.
The overwhelming reaction from Iron-based compounds classifies them as ferromagnetic. These are materials that retain magnetism even in the absence of a magnetic field. Paramagnetic substances like Tungsten and liquid Oxygen are weakly magnetized due to the presence of unpaired electrons. They lose their magnetism once the magnetizing force is removed.
Diamagnetic substances have no unpaired electrons and are magnetized in the opposite direction. They are weakly repelled as the pairing of electrons cancels out the magnetic moments resulting in the loss of magnetic character.
Is Titanium Magnetic?
To determine whether tungsten is paramagnetic or diamagnetic, we must first familiarize ourselves with its electronic configuration. As mentioned earlier, the presence of unpaired electrons in an element is indicative of paramagnetism. Tungsten has an atomic number of 74 and is in group 6 of the periodic table. It has an electronic configuration of [Xe] 6s²4f¹⁴5d⁴. An orbital diagram is presented below:
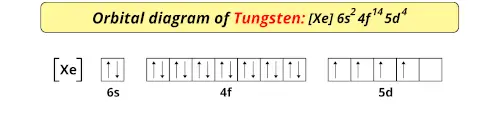
From the figure, we observe that there are four unpaired electrons in the 5d orbital. These unpaired electrons align parallel to an applied field producing a weak magnetic effect. Therefore, Tungsten is magnetic and can be classified as a Paramagnetic substance.
Properties Of Titanium
Titanium is strong and can be compared to steel but it is lighter than steel, making it a better choice for a few applications.
- Ductile
- Low density
- Strong
- Metallic-white
- Lustrous
- Refractory
- Paramagnetic
- Low thermal and electric conductivity
- Resistant to corrosion
- Non-toxic
Applications Of Titanium
Besides surgical procedures, titanium has a wide range of applications as a compound or an alloy. Let’s take a look at a few of them:
- Manufacturing pigments for house paints, plastics, paper, enamel, etc.
- Making smoke screens
- Producing polypropylene
- Sunscreens
- Desalination of plants
- Aircraft and space crafts
- Tooth implants and joint replacements
Concluding Remarks
- Tungsten is a rare earth metal with an atomic number of 74
- It has an electronic configuration of [Xe] 6s² 4f¹⁴ 5d⁴ and possesses 4 unpaired electrons.
- Due to the presence of unpaired electrons, tungsten is weakly magnetized by a magnetic field and can be classified as Paramagnetic.
People Also Ask
1. Is Titanium Okay For MRI?
Yes, the fact that it is non-magnetic makes it a safe choice for MRI.
2. Can Titanium Be Scratched?
Yes, the metal is not scratch-resistant.
3. Will Titanium Set Off A Metal Detector?
No, it won’t.
4. Are All Dental Implants Titanium?
Most of them are. Only if you are allergic to titanium, another metal may be used.
5. What Can Damage Titanium?
Fluoride has the ability to damage titanium.
6. Does Titanium Turn Black?
No, it does not.




This was really helpful in understanding magnetic and other properties of Ti! Also for understanding the differences between paramagnetism and diamagnetism. However it looks like there is some information sprinkled in here about Tungsten W that might not belong? Thank you Priyanka! 🙂
Hi Alan,
Glad you like the article. I might have missed out on a few details, and as a human, I make mistakes, so if you find a helpful element that must be included in the article, please share it with all the readers in the comments and me.
Thank You for reading my article!