Beryllium Dichloride, having a chemical formula of BeCl2 is an inorganic and colourless compound. It dissolves in a lot of polar solvents. BeCl2 is used in the electrolysis reactions for Beryllium. The compound is made up of one Beryllium atom and two Chlorine atoms. To understand the physical and chemical properties of any molecule, one needs to know the molecular geometry and the Lewis structure.
| Name of molecule | Beryllium Dichloride (BeCl2) |
| No of Valence Electrons in the molecule | 16 |
| Hybridization of BeCl2 | sp hybridization |
| Bond Angles | 180° |
| Molecular Geometry of BeCl2 | Linear |
In this blog post, we will look at the Lewis structure of BeCl2, its molecular geometry, bond angles, shape and more.
Contents
BeCl2 Valence electrons
To determine the Lewis structure of any molecule, we must know the total number of valence electrons for the molecule. We will first find out the total valence electrons for BeCl2 and then go through its Lewis Structure.
Total number of valence electrons in BeCl2 – Valence electrons of Be + Valence electrons of Cl
Beryllium has 2 valence electrons in its outer shell.
Chlorine has 7 valence electrons, but as there are two atoms of chlorine, we will multiply the number by 2.
Total number of valence electrons in BeCl2– 2 + 7*2
= 16
Thus, BeCl2 has 16 valence electrons.
BeCl2 Lewis Structure
The Lewis structure of any given molecule helps to know the arrangement of atoms in the molecule, bond formations and the lone pairs. All these characteristics help in determining other properties of the molecule.
Any given atom follows the octet rule, although there are some exceptions to this rule. The octet rule states that an atom must have 8 electrons in its outer shell to attain a stable structure similar to the inert gases. Thus, each atom tries to get eight valence electrons in its outer shell by sharing the other atoms’ electrons.
The electrons that participate in forming bonds are called bonding pairs of electrons, whereas the ones that do not take part in bonds are known as the lone pairs of nonbonding pairs of electrons.
For BeCl2, Beryllium will take the central position as it is less electronegative than chlorine atoms. So place the Be atom in the centre with both the Chlorine atoms on the side.
If you look at the Chlorine atoms, both these atoms require one valence electron to complete their octet. Beryllium will share one valence electron each with the Chlorine atoms so that both the atoms can complete their octet.
Hence all the valence electrons are used up, and there are no lone pairs of electrons in this molecule. There are two bonded pairs of electrons on the central Beryllium atom. The bonds formed between Chlorine and Beryllium are covalent as both these atoms are sharing their electrons.

BeCl2 Hybridization
The electron configuration of Be in its ground state is 1s2 2s2. In this molecule, Beryllium shares both the valence electrons in its outer shell with Chlorine atoms. The electrons in 2s get unpaired in its excited state, and one electron moves to the 2p orbital. As a result, there are two hybrid orbitals formed: one s orbital and one p orbital. Thus, hybridization of Be is sp for BeCl2 in its monomeric form.
BeCl2 Bond Angles
All the atoms of this molecule are arranged in a single plane. BeCl2 has a symmetric arrangement as both the Chlorine atoms are on either side of the central atom. And both these atoms share one valence electron of Beryllium to complete their octet. The bond angle of Cl-Be-Cl is 180° as there are no lone pairs in the molecule.

BeCl2 Molecular Geometry
BeCl2 has an easy structure and molecular geometry. Beryllium forms single covalent bonds with both the Chlorine atoms. These bonded pairs of electrons take the positions as far as possible to avoid the repulsive forces, resulting in 180° bond angle. And as all the electrons are used up, and there are no lone pairs, the molecular geometry of BeCl2 is linear.
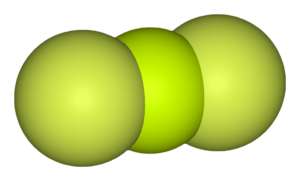
BeCl2 Shape
As mentioned above, BeCl2 has a linear geometry to minimize the repulsive forces between the bonded pairs of electrons. This arrangement of electrons and atoms in the molecule makes the shape of BeCl2 linear.
Concluding Remarks
For a quick revision and summary, we can conclude the following for Beryllium Dichloride:
- It consists of one Beryllium atom and two Chlorine atoms.
- Beryllium forms single covalent bonds with both Chlorine atoms; thus, there are two bonded pairs of electrons on the central atom.
- There are no lone pairs of electrons in this molecule as all electrons are used up.
- BeCl2 has sp hybridization and linear molecular geometry.
- The bond angles of Cl-Be-Cl is 180°.