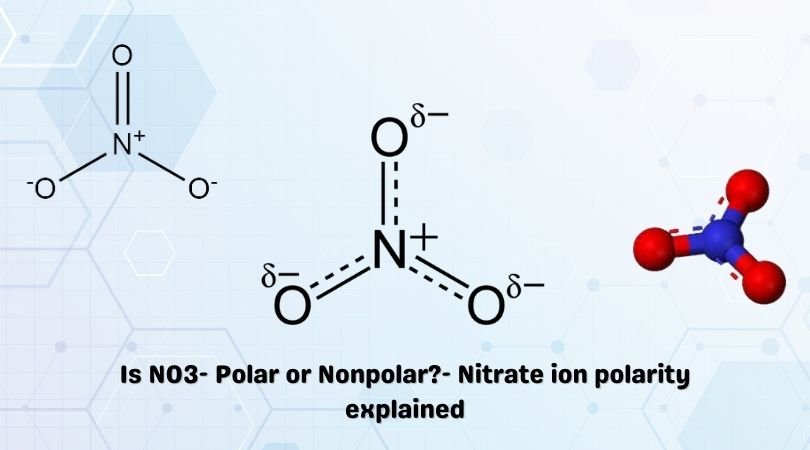
The chemical formula NO3– represents the Nitrate ion. It is derived from Nitric acid, HNO3. Salts containing the Nitrate ion are referred to as ‘Nitrates‘. These salts exist abundantly in nature and find themselves used in a variety of applications.

A diet rich in Nitrate elevates endurance and increases plasma levels. This increase helps regulation of blood flow in the muscles. Nitrates naturally occur in the soil. They find use in fertilizers and explosives among other things.
We say that the Nitrate ion is non-polar. Let’s see why that is the case.
To determine the polarity of the NO3– ion, we must first account for its properties. These include its electronegativity, its molecular geometry, and its resulting dipole moment if any.
Electronegativity and Bond Nature
To determine if the bonds present in the NO3– ion are polar or non-polar, we look to the periodic table. The difference in charges between the Nitrogen and Oxygen atoms is .40
Now, in accordance with the Pauling scale, this tells us that the Nitrogen-Oxygen bond in the NO3– ion is non-polar.
Molecular Shape and Symmetry
The NO3– ion has three Oxygen atoms bonded to the central Nitrogen atom as shown in the figure.
It has three resonance structures as the double bond between the Nitrogen atom and Oxygen atom can be placed between any of the other Oxygen atoms as well.

According to the VSEPR theory, the Oxygen atoms repel each other and spread far away in an even manner. This results in equivalent bond angles of 120°, making the structure symmetrical. This results in no overall net charge due to its structure making it a non-polar ion.
Net Dipole Moment and 1- Charge
The 1- charge over the entire molecule is distributed evenly. It interacts with polar solvents such as water due to this charge. This is even though it is structurally non-polar.

In the averaged out resonance structure, the negative charge is distributed evenly as shown in the figure.
In three dimensions, it can be seen that the dipoles on the bonds all point in opposite directions. This leads to a zero net dipole moment.
Using the above, we can safely say that the Nitrate ion is non-polar.
Conclusion
As shown above, the NO3– ion has an overall 1- charge. However, this negative charge is distributed evenly due to its symmetric shape. This results in a zero net dipole moment. Further, the Nitrogen- Oxygen bonds are non-polar according to the Pauling scale.
Therefore, the NO3– ion non-polar in nature.