Carbon Dioxide, or CO2, is one of the most known gases due to its contribution to the greenhouse effect and global warming. Keeping all that aside, it is a colorless gas that is used in several industries today, right from refrigerants to fire extinguishers, plastic, and more.
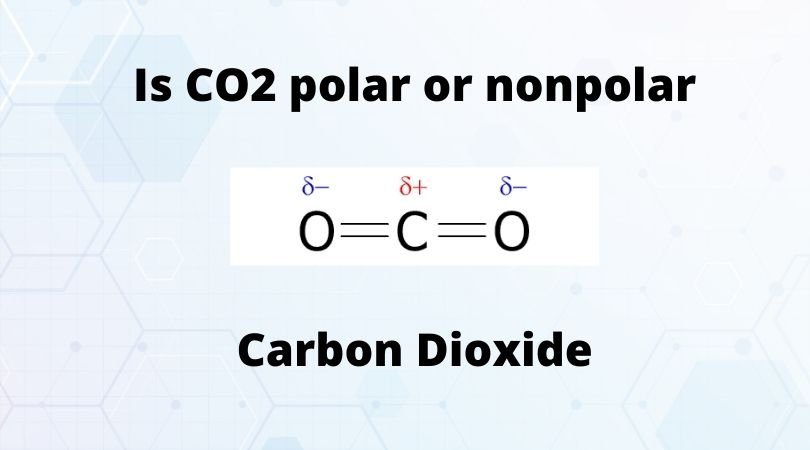
The gas is made of two types of atoms – Carbon and Oxygen. Each CO2 molecule has two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom. If you study the CO2 Lewis structure and its molecular geometry, you will know that the Carbon atom is in the central position forming double bonds with both Oxygen atoms. This structure can help us understand the polarity of this molecule.
For those who know what polarity is, here is a brief description that can help you with understanding what this property is:
What is polarity?
Any molecule that we discuss has atoms that either has regions of positive charges or negative charges. The atom that donates electrons has positive charges, whereas the ones accepting the electrons have negative charges.
Polarity is the property or term used to define these positive and negative electric charges in the molecule. Any molecule having a negative-charged atom and a positively charged atom has an electric dipole moment. And this dipole moment is used to know if the molecule is polar or nonpolar.
When the electrons are arranged in a symmetric pattern in a given molecule, the charges on both the atoms cancel out the dipole moment, and hence they become nonpolar. However, these charges are not canceled out when there is an asymmetric distribution of electrons. Due to this dipole moment, the most electronegative atom in the molecule tries to pull the charges towards it, leading to the dipole moment between these atoms, making a molecule polar.
Symmetric molecules have no net dipole moment; hence they are nonpolar. In contrast, asymmetric molecules have a dipole moment, which makes them polar.
Is CO2 polar or nonpolar?
When it comes to Carbon Dioxide, it has a linear geometry as both the Oxygen atoms share double bonds with the central Carbon atom. All the charges are equally distributed, and both the bond dipole moments are canceled.
Hence as there is no net molecular dipole moment in the molecules, CO2 is a nonpolar molecule.
Concluding Remarks
Generally, the molecules with a symmetric distribution of charges are nonpolar as there is no net dipole moment in the molecules. As the atoms have equal pulls on the electrons and charge distribution is uniform, the molecules with symmetrical distribution are nonpolar. In CO2, as the electrons are evenly distributed, and there is no dipole moment in the molecule, it is a nonpolar molecule.